Reviewer: S. Randhawa, M.D., Allergist/Immunologist and Assistant Professor at LSU (Shreveport) Department of Allergy and Immunology
Fc receptor is a protein found on the surface of cells that binds to a part of an antibody known as the Fc (Fragment, crystallizable) region. Each Fc receptor functions as a receptor specific for the CH region of the Ig molecule.
An antibody has Fab (fragment, antigen-binding) and Fc (fragment, crystalizable) regions. Fc receptors bind to the Fc region. Image source: Wikipedia, public domain.
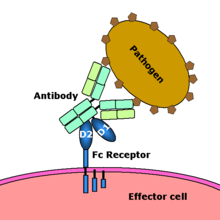
Fc receptor interaction with an antibody-coated microbial pathogen. Image source: Wikipedia, public domain.
The uptake of bacteria by phagocytes is an active process, which requires the triggering of specific receptors on the phagocyte. Fc receptors, which bind antibody-coated bacteria, are one of the receptors capable of triggering phagocytosis. This video is from: Janeway's Immunobiology, 7th Edition Murphy, Travers, & Walport. Source: Garland Science.
There are several different types of Fc receptors, which are classified based on the type of antibody that they recognize. The Latin letter used to identify a type of antibody is converted into the corresponding Greek letter, which is placed after the 'Fc' part of the name:
- Fc that bind the most common class of antibody, IgG, are called Fc-gamma receptors (FcγR)
- Fc that bind IgA are called Fc-alpha receptors (FcαR)
- Fc that bind IgE are called Fc-epsilon receptors (FcεR)
Fc gamma receptors for IgG are CD 16, 32, 64 (double). IgG is transported across the placenta by an IgG-specific Fc receptor called neonatal Fc receptor (FcRn), which resembles a MHC class I molecule. CD16 (FcR-gamma-III) is the most common IgG Fc receptor. CD32 down-regulates IgG. Binding of FcγRIIb is the proposed mechanism of action of IVIG.
Fc gamma receptors for IgG (CD 16, 32, 64) are labeled in "reverse" order:
CD 16 - FcR III - low-affinity
CD 32 - FcR II - intermediate-affinity
CD 64 - FcR I - high-affinity
CD16 and CD56 are present on NK cells. CD16 and CD14 are present on macrophages.
Fc II receptors:
CD 32 - Fc gamma II
CD 23 - Fc epsilon II, Fc receptors for IgE
CD23 is the low affinity IgE receptor (FceRII). CD21 (CR2) binds EBV, HHV8, C3d, and CD23 (low affinity IgE receptor (FceRII).
CD32 down-regulates IgG. Binding of FcγRIIb is the proposed mechanism of action of IVIG.
Immunomodulating effects of IVIG mediated through Fc receptor blockade
- ADCC inhibition by blockade of FcγRIII (CD16) on NK cells
- Inhibition of antibody production by blockade of FcγRIIb (CD32) on B cells
- IVIG blocks membrane Fc receptors on phagocytic cells in spleen and liver in patients with ITP
Place in order the CD designation and the Fc receptor starting with FcγRI, FcγRII, FcγRIII, FceRII:
A. CD23, CD16, CD32, CD64
B. CD64, CD32, CD16, CD23
C. CD64, CD16, CD32, CD23
D. CD16, CD32, CD64, CD23
Answer: B.
Fc receptor. Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia.
No comments:
Post a Comment