Reviewer: S. Randhawa, M.D., Fellow, LSU (Shreveport) Department of Allergy & Immunology
Sialyl LewisX (SLeX, CD15) is a tetrasaccharide carbohydrate attached to O-glycans on the surface of the cells that plays a vital role in cell-cell recognition processes. Sialyl Lewis X is also a blood group antigen. CD15 is a carbohydrate adhesion molecule (not a protein) that mediates phagocytosis and chemotaxis.
Granulocytes are CD45+ CD15+ cells. Monocytes are CD45+ CD14+ cells.

Sialyl LewisX (SLeX). Image source: Wikipedia, public domain.
Sialyl Lewis X determinant, E-selectin ligand carbohydrate structure, is expressed on granulocytes and monocytes and mediates extravasation. Defective synthesis of Sialyl Lewis X can be caused by defects in fucose metabolsims.

Fucose is a hexose deoxy sugar. Image source: Wikipedia, GNU Free Documentation License.
Leukocyte Extravasation. This video describes how a leukocyte moves out of the endothelium of a blood vessel. This video is from: Janeway's Immunobiology, 7th Edition Murphy, Travers, & Walport. Source: Garland Science.
LAD type 2
There is inability to put sialyl-LewisX (SLeX) cap on leukocytes. CD15 (SLeX) is found on neutrophils; expressed in patients with Hodgkin disease, some B-cell CLL, ALL, and most AML.
LAD type 2
CD15
F
Fifteen
Fucose, Sialyl LewisX (SLeX)
FucT-1 gene
CD18
CD18 helps neutrophils make their way from the blood stream into the infected areas of the body.
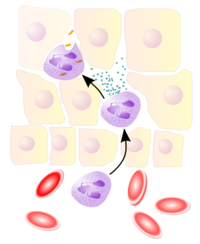
Neutrophils extravasate from blood vessels to the site of tissue injury or infection during the innate immune response. Image source: Wikipedia, GNU Free Documentation License.
CD18 is the beta subunit of 3 different structures (paired with CD11 a, b, c):
- LFA-1 (paired with CD11a)
- Macrophage-1 antigen, MAC-1 (paired with CD11b)
- Integrin alphaXbeta2 (paired with CD11c)
CD11a - Subunit of LFA-1, a membrane glycoprotein that provides cell-cell adhesion by interaction with ICAM-1. Lymphocyte function-associated antigen 1 (LFA-1) consists of an alpha-chain (CD11a) and beta-chain (CD18).
CD11b - Subunit of MAC-1, a complement receptor (CR3). MAC-1 consists of an alpha-chain (CD11b) and beta-chain (CD18).
CD11c - Integrin alphaXbeta2 is a subunit of the complement receptor CR4. CR4 consists of an alpha-chain (CD11c) and beta-chain (CD18). CD11c is expressed in hairy cell leukemias, acute nonlymphocytic leukemias, and some B-cell CLL. CD11c is one of the defining markers for dendritic cells.
The integrin superfamily consists of 30 proteins that promote cell-cell or cell-matrix interactions. The name integrins derives from the idea that they coordinate (i.e., "integrate") signals.
All integrins are cell surface proteins composed of 2 polypeptide chains, α and β.
Integrins are classified into several subfamilies based on the β chains.
The β1-containing integrins are also called VLA molecules. VLA ("very late antigens") received their name because α1β1 and α2β1 were expressed on T cells 2 to 4 weeks after repetitive stimulation in vitro in the early experiments.
The β1 integrins are also called CD49a-fCD29. CD49a-f refers to different α chains (α1 to α6). CD29 refers to the common β1 subunit.
The β2 integrins are also known as the LFA-1 family or CD11a-cCD18. CD11 refers to different α chains and CD18 to the common β2 subunit. LFA-1 is also called CD11aCD18.
Other members of the LFA-1 family include CD11bCD18 (Mac-1 or CR3) and CD11cCD18 (p150,95 or CR4), both of which have the same β subunit as LFA-1.
LAD type 1
First recognized as a distinct clinical entity in the 1970s. The inherited molecular defect in patients with LAD type 1 is a defect in CD18. CD18 is the β2 chain (β-2 integrin subunit) common to LFA-1 and MAC-1.
Adhesion Molecules

Overview of adhesion molecules, 3 groups remembered by the mnemonic SIS.
Neutrophils (PMN) are the most numerous among peripheral leukocytes (70%) and are the first line of defense against pathogens. PMN circulate in the blood for only 6 hours. PMN migration is regulated via adhesion molecules.
Recruitment of Leukocytes to Sites of Infection
SIP of wine:
Selectins
Integrins
Penetration of BM by PMN
Selectins are first in the chain of events. They upregulate TNF and IL-1.
Integrins cause release of VCAM and VLA.
Adhesion molecules, 3 groups = SIS
Selectins
Integrins
Superfamily Ig
Selectins
The name selectin comes from the words "selected" and "lectins." Selectins are a type of carbohydrate-recognizing proteins.
There are 3 groups of selectins = LEP
L-selectins, CD62L
Leukocytes
E-selectins, CD62E
Endothelial cells
P-selectins, CD62P
Platelets

Selectin E (endothelial adhesion molecule 1). Image source: Wikipedia.
CD62E - E-selectin is a cell adhesion molecule expressed only on endothelial cells activated by cytokines.
CD62L - L-selectin is a cell adhesion molecule found on leukocytes.
CD62P - P-selectin is a cell adhesion molecule (CAM) found in granules in endothelial cells (cells lining blood vessels) and activated platelets.
CD markers for central vs. effector memory T cells:
Central memory T cells: CD45RA-, CD27+, CCR7+, CD62L+
Effector memory T cells: CD45RA-, CD27-, CCR7-, CD62L-
LAD type 1 is a problem of PMNs binding to integrins (LAF-1). Integration (tight adhesion) is the second phase of the PMN recruitment (see the "SIP" mnemonic above). LAD type 2 is a problem of PMNs binding to selectins. Selection ("rolling") is the first phase of the PMN recruitment (see the "SIP" mnemonic above).
Integrins
LFA (leukocyte function Ag), VLA (very late Ag). For example, LFA 1-3 bind to CD (cluster of differentiation) cell adhesion molecules on the surface of T cells.
Ig Superfamily = cell adhesion molecules (CAM)
VIP:
VCAM (vascular cell adhesion molecule)
ICAM (intercellular adhesion molecule)
PECAM (platelet-endothelial cell adhesion molecule)

Intercellular adhesion molecule 2 (ICAM 2). Image source: Wikipedia.
Leukocyte adhesion deficiency II (LAD2 ) is characterized by which of the following?
(A) X-linked inheritance
(B) neutropenia
(C) hypogammaglobulinemia
(D) severe mental retardation
(E) autosomal recessive inheritance
(F) CD18 defect
(G) Sialyl LewisX-related defect
Answers: D, E, G. LAD1 is related to CD18 defect.
References
Leukocyte adhesion deficiency. Wikipedia.
CD18. Wikipedia.
Sialyl Lewis X. Wikipedia.
Published: 05/18/2009
Updated: 08/18/2010
No comments:
Post a Comment