Reviewer: S. Randhawa, M.D., Fellow, LSU (Shreveport) Department of Allergy & Immunology
CD44
CD45 - leukocyte common antigen, present on all hemopoietic cells except erythrocytes
CD44 is a cell-surface glycoprotein involved in cell-cell interactions, cell adhesion and migration. PMN adhesion to the endothelium is mediated through CD44.
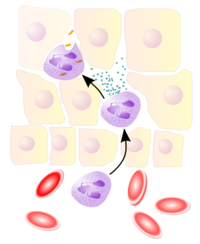
Neutrophils extravasate from blood vessels to the site of tissue injury or infection during the innate immune response. Image source: Wikipedia, GNU Free Documentation License.
CD44 is a receptor for hyaluronic acid. A specialized sialofucosylated glycoform of CD44 called HCELL is found natively on human hematopoietic stem cells, and is a highly potent E-selectin and L-selectin ligand. HCELL functions as a "bone homing receptor", directing migration of human hematopoietic stem cells and mesenchymal stem cells to bone marrow.
CD44 expression is an indicative marker for effector-memory T-cells.
CD44
CD99
Both participate in leukocyte migration.
T and B Cells - Naive and Memory Cell Markers (click to enlarge the image).
References
Cluster of differentiation (CD) of leukocytes
CD44, Wikipedia.
Published: 05/18/2009
Updated: 05/18/2009
No comments:
Post a Comment