Editor: V. Dimov, M.D., Allergist/Immunologist, Assistant Professor at University of Chicago
How to Use the Nebulizer Machine (albuterol, Xopenex, budesonide) - Demonstration Video. This video is an excerpt from the DVD Living With Asthma: A Guide to Controlling Your Asthma produced by St. Louis Children's Hospital:
How to Use a Nebulizer, from National Jewish Hospital: http://bit.ly/VCjfAp
How to Use a Metered Dose Inhaler (albuterol, Flovent, Symbicort, Dulera) - Demonstration Video. This video is an excerpt from the DVD Living With Asthma: A Guide to Controlling Your Asthma produced by St. Louis Children's Hospital:
How to Use the a Twisthaler (Asmanex) - Demonstration Video from National Jewish Hospital:
How to Use a Diskus Inhaler (Advair or Flovent) - Demonstration Video. This video is an excerpt from the DVD Living With Asthma: A Guide to Controlling Your Asthma produced by St. Louis Children's Hospital:
How to Use a Diskus, from National Jewish Hospital: http://bit.ly/VCiOpE
How to Use the a Flexhaler (Pulmicort) - Demonstration Video. This video is an excerpt from the DVD Living With Asthma: A Guide to Controlling Your Asthma produced by St. Louis Children's Hospital:
Related videos and information
How to Use an Inhaler. ACP.
How to Use an Inhaler with a Spacer. ACP.
How to Use a Diskus Inhaler. ACP.
Published: 02/07/2011
Updated: 10/21/2012
Showing posts with label Video. Show all posts
Showing posts with label Video. Show all posts
How to use a spacer device for inhalation
Editor: V. Dimov, M.D., Allergist/Immunologist, Assistant Professor at University of Chicago
How to Use a Metered Dose Inhaler with a Spacer (albuterol, Xopenex, Flovent, Symbicort, Dulera) - Demonstration Video. This video is an excerpt from the DVD Living With Asthma: A Guide to Controlling Your Asthma produced by St. Louis Children's Hospital:
Aerochamber, from National Jewish http://bit.ly/VClaF0
How to Use an AeroChamber with a Face Mask for Chidlren Younger than Age 5 (albuterol, Xopenex, Flovent) - Demonstration Video. This video is an excerpt from the DVD Living With Asthma: A Guide to Controlling Your Asthma produced by St. Louis Children's Hospital:
Aerochamber with Mask, from National Jewish http://bit.ly/VClfIW
For older children and adults: How to use a metered dose asthma inhaler - open mouth technique for albuterol, Xopenex, Flovent, Symbicort, Dulera. Watch this American Lung Association video to learn the correct way to use your metered dose (MDI) asthma inhaler:
For older children and adults: How to use a metered dose asthma inhaler with a spacer or valved holding chamber (albuterol, Xopenex, Flovent, Symbicort, Dulera). Watch this American Lung Association video to learn the correct way to use your metered dose (MDI) asthma inhaler:
Published: 02/07/2011
Updated: 10/21/2012
How to Use a Metered Dose Inhaler with a Spacer (albuterol, Xopenex, Flovent, Symbicort, Dulera) - Demonstration Video. This video is an excerpt from the DVD Living With Asthma: A Guide to Controlling Your Asthma produced by St. Louis Children's Hospital:
Aerochamber, from National Jewish http://bit.ly/VClaF0
How to Use an AeroChamber with a Face Mask for Chidlren Younger than Age 5 (albuterol, Xopenex, Flovent) - Demonstration Video. This video is an excerpt from the DVD Living With Asthma: A Guide to Controlling Your Asthma produced by St. Louis Children's Hospital:
Aerochamber with Mask, from National Jewish http://bit.ly/VClfIW
For older children and adults: How to use a metered dose asthma inhaler - open mouth technique for albuterol, Xopenex, Flovent, Symbicort, Dulera. Watch this American Lung Association video to learn the correct way to use your metered dose (MDI) asthma inhaler:
For older children and adults: How to use a metered dose asthma inhaler with a spacer or valved holding chamber (albuterol, Xopenex, Flovent, Symbicort, Dulera). Watch this American Lung Association video to learn the correct way to use your metered dose (MDI) asthma inhaler:
Published: 02/07/2011
Updated: 10/21/2012
How To Use Epinephrine Autoinjector - Auvi-Q or EpiPen
Editor: V. Dimov, M.D., Allergist/Immunologist, Assistant Professor at University of Chicago
This 2-minute video shows the Sanofi's new voice guided Auvi-Q epinephrine injector in action:
Start here: How to use EpiPen. Self-injectable epinephrine (SIE) in the form of a device (EpiPen) was first introduced in 1980.
Video instructions on use of the EpiPen (epinephrine/adrenaline) autoinjector for anaphylaxis from the Australasian Society of Clinical Immunology and Allergy (ASCIA):
How To Use an EpiPen video from Nationwide Children's Hospital in Columbus, Ohio:
Tips for managing food allergy (MJA, 2004):
- Always carry an EpiPen 2-Pak
- Always read food labels
- Ask questions about food preparation (be aware of the risk of cross-contamination)
- No label/no eat
- No EpiPen/no eat
- Tell friends about a serious food allergy
- Tell friends if feeling unwell, especially after eating
The action plans for food allergy and anaphylaxis include the use of EpiPen as first line of treatment.
Key points:
- There is no cure for food allergies at this time
- 8% of U.S. children under 18 have at least one food allergy
- Epinephrine is the first line life-saving medication in severe food allergic reaction. Always carry an EpiPen with you, and remember these simple memory rules in severe food allergic reaction:
- "No Epi, no eat-y" (always carry an EpiPen with you, don't sit down to eat if you don't have an EpiPen available)
- "If it's more than the skin, the Epi goes in" (only mild hives may respond to antihistamine, for anything else you may need an EpiPen)
References
How to use Epipen (official video)
Official EpiPen App for iPhone and iPad
Action plans: asthma, food allergy, rhinitis, anaphylaxis
Training of trainers on epinephrine autoinjector use increases correct use from 23.3% to 74.2% http://goo.gl/lMfSR
Food allergy and anaphylaxis training - free at AllergyReady.com
Time epinephrine needs to reach muscle - holding the device in place for 1 second is as effective as 10 seconds. Annals of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology, 2011.
Related reading
"Epinephrine is to anaphylaxis as an AED (defibrillator) is to someone suffering cardiac arrest. Life-saving." Forbes, 2012.
Published: 01/29/2011
Updated: 05/12/2012
This 2-minute video shows the Sanofi's new voice guided Auvi-Q epinephrine injector in action:
Start here: How to use EpiPen. Self-injectable epinephrine (SIE) in the form of a device (EpiPen) was first introduced in 1980.
Video instructions on use of the EpiPen (epinephrine/adrenaline) autoinjector for anaphylaxis from the Australasian Society of Clinical Immunology and Allergy (ASCIA):
How To Use an EpiPen video from Nationwide Children's Hospital in Columbus, Ohio:
Tips for managing food allergy (MJA, 2004):
- Always carry an EpiPen 2-Pak
- Always read food labels
- Ask questions about food preparation (be aware of the risk of cross-contamination)
- No label/no eat
- No EpiPen/no eat
- Tell friends about a serious food allergy
- Tell friends if feeling unwell, especially after eating
The action plans for food allergy and anaphylaxis include the use of EpiPen as first line of treatment.
Key points:
- There is no cure for food allergies at this time
- 8% of U.S. children under 18 have at least one food allergy
- Epinephrine is the first line life-saving medication in severe food allergic reaction. Always carry an EpiPen with you, and remember these simple memory rules in severe food allergic reaction:
- "No Epi, no eat-y" (always carry an EpiPen with you, don't sit down to eat if you don't have an EpiPen available)
- "If it's more than the skin, the Epi goes in" (only mild hives may respond to antihistamine, for anything else you may need an EpiPen)
References
How to use Epipen (official video)
Official EpiPen App for iPhone and iPad
Action plans: asthma, food allergy, rhinitis, anaphylaxis
Training of trainers on epinephrine autoinjector use increases correct use from 23.3% to 74.2% http://goo.gl/lMfSR
Food allergy and anaphylaxis training - free at AllergyReady.com
Time epinephrine needs to reach muscle - holding the device in place for 1 second is as effective as 10 seconds. Annals of Allergy, Asthma and Immunology, 2011.
Related reading
"Epinephrine is to anaphylaxis as an AED (defibrillator) is to someone suffering cardiac arrest. Life-saving." Forbes, 2012.
Published: 01/29/2011
Updated: 05/12/2012
Saline Sinus Rinse/Flush - Patient Education Videos
Editor: V. Dimov, M.D., Allergist/Immunologist, Assistant Professor at University of Chicago
Saline nasal irrigation bathes the nasal cavity with liquid by instilling saline into 1 nostril and allowing it to drain out of the other nostril (typically, it drains from both nostrils and the mouth). Only use sterile, distilled, filtered water (using a filter with an absolute pore size of 1 μm or smaller), or previously boiled water for nasal irrigation.
NeilMed Sinus Rinse Video.
Pediatric Nasal Saline Flush/Rinse. Fauquier ENT | January 28, 2008 | This video shows a young child performing saline flushes to his nose without assistance. Indeed, kids older than 5 years are able to perform flushes without difficulty.
Adult Saline Sinus Rinse/Flush. Fauquier ENT | December 05, 2007 | Patient performing a saline flush to his nose. This procedure is often performed by patients who have chronic sinusitis or allergies.
Techniques and devices
Techniques and devices include:
- low positive pressure from a spray or squirt bottle
- gravity-based pressure using a neti pot or other vessel with a nasal spout
Indications
A range of conditions may respond to saline nasal irrigation but the evidence supporting its use is less conclusive:
- allergic rhinitis
- acute upper respiratory tract infections (URTI)
- rhinitis of pregnancy
- acute rhinosinusitis
The exact mechanism of action of saline nasal irrigation is unknown. Saline nasal irrigation may improve nasal mucosa function through direct cleansing; removal of inflammatory mediators, and improved mucociliary function, as suggested by increased ciliary beat frequency.
Adverse effects
Fewer than 10% of patients reported adverse effects:
- self-limited sensation of ear fullness
- "stinging" of the nasal mucosa
- rarely epistaxis
-infections. Louisiana Department of Health and Hospitals warned against improper use following the deaths of two people who were infected with Naegleria fowleri after using tap water to irrigate their sinuses. Read more here: Is Rinsing Your Sinuses Safe?
Contraindications
Contraindications for saline nasal irrigation include:
- incompletely healed facial trauma
- increased risk for aspiration, such as intention tremor or other neurologic or musculoskeletal problems.
Recommendations
- For chronic rhinosinusitis, nasal irrigation is an effective adjunctive therapy (level of evidence, A).
- Limited evidence for effective adjunctive treatment of irritant or allergic rhinitis, viral upper respiratory tract infection, and postoperative care after endoscopic sinus surgery (level of evidence, B).
- rhinitis of pregnancy, acute rhinosinusitis, sinonasal sarcoidosis, and Wegener's granulomatosis (level of evidence, C).
Mayo Clinic: What can you do about that runny nose and nasal congestion? Medications are one option, but so is nasal cleansing.
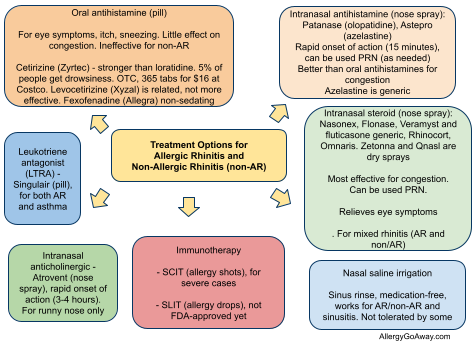
Treatment Options for Allergic Rhinitis (click to enlarge the image).
References
Use of Saline Nasal Irrigation Reviewed. Laurie Barclay, MD. Medscape, 2009.
Saline Nasal Irrigation for Upper Respiratory Conditions. Am Fam Physician. 2009 November 15; 80(10): 1117–1119 (PDF).
SinuSurf (nasal saline rinse with surfactant) associated with loss of smell "for months to years". Discontinue use (PDF) http://goo.gl/awQUP
Neti Pot, Nasal Irrigation - Pros and Cons and Slideshow. WebMD, 2011.
North Louisiana Woman Dies from Rare Ameba Infection. DHH warns residents about improper neti pot use, 2011.
Is Rinsing Your Sinuses Safe? FDA replies: http://goo.gl/XL5bJ
Chronic sinus infections with mycobacteria associated with sinus rinses with tap water (nasal washing) http://goo.gl/wiV12
Published: 02/07/2011
Updated: 08/27/2012
Saline nasal irrigation bathes the nasal cavity with liquid by instilling saline into 1 nostril and allowing it to drain out of the other nostril (typically, it drains from both nostrils and the mouth). Only use sterile, distilled, filtered water (using a filter with an absolute pore size of 1 μm or smaller), or previously boiled water for nasal irrigation.
NeilMed Sinus Rinse Video.
Pediatric Nasal Saline Flush/Rinse. Fauquier ENT | January 28, 2008 | This video shows a young child performing saline flushes to his nose without assistance. Indeed, kids older than 5 years are able to perform flushes without difficulty.
Adult Saline Sinus Rinse/Flush. Fauquier ENT | December 05, 2007 | Patient performing a saline flush to his nose. This procedure is often performed by patients who have chronic sinusitis or allergies.
Techniques and devices
Techniques and devices include:
- low positive pressure from a spray or squirt bottle
- gravity-based pressure using a neti pot or other vessel with a nasal spout
Indications
A range of conditions may respond to saline nasal irrigation but the evidence supporting its use is less conclusive:
- allergic rhinitis
- acute upper respiratory tract infections (URTI)
- rhinitis of pregnancy
- acute rhinosinusitis
The exact mechanism of action of saline nasal irrigation is unknown. Saline nasal irrigation may improve nasal mucosa function through direct cleansing; removal of inflammatory mediators, and improved mucociliary function, as suggested by increased ciliary beat frequency.
Adverse effects
Fewer than 10% of patients reported adverse effects:
- self-limited sensation of ear fullness
- "stinging" of the nasal mucosa
- rarely epistaxis
-infections. Louisiana Department of Health and Hospitals warned against improper use following the deaths of two people who were infected with Naegleria fowleri after using tap water to irrigate their sinuses. Read more here: Is Rinsing Your Sinuses Safe?
Contraindications
Contraindications for saline nasal irrigation include:
- incompletely healed facial trauma
- increased risk for aspiration, such as intention tremor or other neurologic or musculoskeletal problems.
Recommendations
- For chronic rhinosinusitis, nasal irrigation is an effective adjunctive therapy (level of evidence, A).
- Limited evidence for effective adjunctive treatment of irritant or allergic rhinitis, viral upper respiratory tract infection, and postoperative care after endoscopic sinus surgery (level of evidence, B).
- rhinitis of pregnancy, acute rhinosinusitis, sinonasal sarcoidosis, and Wegener's granulomatosis (level of evidence, C).
Mayo Clinic: What can you do about that runny nose and nasal congestion? Medications are one option, but so is nasal cleansing.
Treatment Options for Allergic Rhinitis (click to enlarge the image).
References
Use of Saline Nasal Irrigation Reviewed. Laurie Barclay, MD. Medscape, 2009.
Saline Nasal Irrigation for Upper Respiratory Conditions. Am Fam Physician. 2009 November 15; 80(10): 1117–1119 (PDF).
SinuSurf (nasal saline rinse with surfactant) associated with loss of smell "for months to years". Discontinue use (PDF) http://goo.gl/awQUP
Neti Pot, Nasal Irrigation - Pros and Cons and Slideshow. WebMD, 2011.
North Louisiana Woman Dies from Rare Ameba Infection. DHH warns residents about improper neti pot use, 2011.
Is Rinsing Your Sinuses Safe? FDA replies: http://goo.gl/XL5bJ
Chronic sinus infections with mycobacteria associated with sinus rinses with tap water (nasal washing) http://goo.gl/wiV12
Published: 02/07/2011
Updated: 08/27/2012
How to use a nose spray
Editor: V. Dimov, M.D., Allergist/Immunologist, Assistant Professor at University of Chicago
How to use your nose spray (video):
1. Gently blow your nose to clear it of mucus before using the medication.
2. Remove the cap and shake the bottle.
3. Hold the pump bottle with your thumb at the bottom and your index and middle fingers on top.
4. The first time you use the pump spray each day, you may have to prime it by squirting a few times into the air until a fine mist comes out.
5. Tilt your head forward slightly. Breathe out slowly.
6. Insert into the nostril and aim the nozzle toward the outside of the nose and away from the nasal septum (the cartiledge which divides our nose in half).
7. Squeeze the pump as you begin to breathe in slowly through your nose.
8. Repeat these steps for the other nostril. If you are using more than one spray in each nostril, follow all these steps again. Try not to sneeze or blow your nose just after using the spray.
Nosebleeds are among the most commonly reported adverse effect of intranasal corticosteroid sprays. However, they tend to result from incorrect positioning of the device ("hitting" the septum in the middle), rather than an adverse reaction to the medication.
Common errors to avoid when using a nose spray include the following:
- forgetting to prime the spray device;
- skipping doses
- wrong head position (should be tilted forward, not back)
- pushing nozzle too hard or too far into the nose;
- blowing nose hard after spraying (the medicine is lost)
- sniffing hard after spraying (the medicine is deposited in the throat instead of the nose)
- using saline sprays or irrigations after using corticosteroid spray, instead of before
The National Asthma Council Australia has instructional 'how to' videos on using your nose spray.
Demonstration of how to use Nasonex intranasal spray correctly (video):
Demonstration of how to use Veramyst intranasal spray correctly (called "Avamys" in Australia):
Demonstration of how to use Rhinocort intranasal spray correctly (video):
Antihistamines offer little help in perennial allergic rhinitis where nasal obstruction may not be histamine mediated. A steroid nose spray may work best in perennial allergic rhinitis, for example, rhinitis caused by allergy to dust mite (http://goo.gl/PL5XH).
References Intranasal corticosteroid spray technique Using your asthma inhaler
Published: 01/12/2011
Updated: 10/09/2012
How to use your nose spray (video):
1. Gently blow your nose to clear it of mucus before using the medication.
2. Remove the cap and shake the bottle.
3. Hold the pump bottle with your thumb at the bottom and your index and middle fingers on top.
4. The first time you use the pump spray each day, you may have to prime it by squirting a few times into the air until a fine mist comes out.
5. Tilt your head forward slightly. Breathe out slowly.
6. Insert into the nostril and aim the nozzle toward the outside of the nose and away from the nasal septum (the cartiledge which divides our nose in half).
7. Squeeze the pump as you begin to breathe in slowly through your nose.
8. Repeat these steps for the other nostril. If you are using more than one spray in each nostril, follow all these steps again. Try not to sneeze or blow your nose just after using the spray.
Nosebleeds are among the most commonly reported adverse effect of intranasal corticosteroid sprays. However, they tend to result from incorrect positioning of the device ("hitting" the septum in the middle), rather than an adverse reaction to the medication.
Common errors to avoid when using a nose spray include the following:
- forgetting to prime the spray device;
- skipping doses
- wrong head position (should be tilted forward, not back)
- pushing nozzle too hard or too far into the nose;
- blowing nose hard after spraying (the medicine is lost)
- sniffing hard after spraying (the medicine is deposited in the throat instead of the nose)
- using saline sprays or irrigations after using corticosteroid spray, instead of before
The National Asthma Council Australia has instructional 'how to' videos on using your nose spray.
Demonstration of how to use Nasonex intranasal spray correctly (video):
Demonstration of how to use Veramyst intranasal spray correctly (called "Avamys" in Australia):
Demonstration of how to use Rhinocort intranasal spray correctly (video):
Antihistamines offer little help in perennial allergic rhinitis where nasal obstruction may not be histamine mediated. A steroid nose spray may work best in perennial allergic rhinitis, for example, rhinitis caused by allergy to dust mite (http://goo.gl/PL5XH).
References Intranasal corticosteroid spray technique Using your asthma inhaler
Published: 01/12/2011
Updated: 10/09/2012
Food Allergy Basics (video)
Editor: V. Dimov, M.D., Allergist/Immunologist, Assistant Professor at University of Chicago
The Food Allergy Action Plan by FAAN is available here and from the FAAN website. You may copy these documents and distribute them freely.
Tips for managing food allergy (MJA, 2004):
- Always carry an EpiPen 2-Pak
- Always read food labels
- Ask questions about food preparation (be aware of the risk of cross-contamination)
- No label/no eat
- No EpiPen/no eat
- Tell friends about a serious food allergy
- Tell friends if feeling unwell, especially after eating
Eleanor Garrow, Vice President of Education and Outreach for FAAN, talks about living with food allergies, 2010.
FAANPAL | October 06, 2010 | A presentation of food allergy basics by Eleanor Garrow, Vice President of Education and Outreach for FAAN.
Related information
Food Allergy Information from ACAAI
Free pamphlets (brochures) from National Institutes of Health - Publications Order Form.
Managing Food Allergy - COFAR video, 2012.
Food Allergy: An Overview for Patients (PDF)
Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Food Allergy in the United States: Executive Summary of the NIAID-Sponsored Expert Panel Report (PDF)
Videos from the KFA channel on YouTube -"Kids With Food Allergies"
Food allergy and anaphylaxis training - free at AllergyReady.com
Published: 02/12/2011
Updated: 05/04/2012
The Food Allergy Action Plan by FAAN is available here and from the FAAN website. You may copy these documents and distribute them freely.
Tips for managing food allergy (MJA, 2004):
- Always carry an EpiPen 2-Pak
- Always read food labels
- Ask questions about food preparation (be aware of the risk of cross-contamination)
- No label/no eat
- No EpiPen/no eat
- Tell friends about a serious food allergy
- Tell friends if feeling unwell, especially after eating
Eleanor Garrow, Vice President of Education and Outreach for FAAN, talks about living with food allergies, 2010.
FAANPAL | October 06, 2010 | A presentation of food allergy basics by Eleanor Garrow, Vice President of Education and Outreach for FAAN.
Related information
Food Allergy Information from ACAAI
Free pamphlets (brochures) from National Institutes of Health - Publications Order Form.
Managing Food Allergy - COFAR video, 2012.
Food Allergy: An Overview for Patients (PDF)
Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Food Allergy in the United States: Executive Summary of the NIAID-Sponsored Expert Panel Report (PDF)
Videos from the KFA channel on YouTube -"Kids With Food Allergies"
Food allergy and anaphylaxis training - free at AllergyReady.com
Published: 02/12/2011
Updated: 05/04/2012
Patient Education Videos in Allergy and Immunology
Patient Education Videos by Focus Medica Pte. Ltd.:
Chronic Asthma
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
Sinusitis
Otitis Media
Published: 03/03/2010
Updated: 03/03/2010
Chronic Asthma
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
Sinusitis
Otitis Media
Published: 03/03/2010
Updated: 03/03/2010
Cellular and Molecular Immunology by Abbas et al: Video Lectures and Q&A
Reviewer: S. Randhawa, M.D., Fellow, LSU (Shreveport) Department of Allergy & Immunology
The textbook Cellular and Molecular Immunology by Abbas et al. explains the experimental observations that form the basis for the science of immunology.
Some links that may help you to get more out of the textbook are listed below:
Video Lectures, Conferences On-Line Allergy (COLA) by Children's Mercy Hospital
Immunology - Abbas Chapter 5: MHC
Immunology - Abbas Chapter 7: Antigen Receptors and Accessory Molecules
Imuunology - Abbas Chapter 8 - Lymphocyte Development
Immunology: Abbas Chapter 9 - T-cell Activation
Immunology: Abbas Chapter 10 - B-cell Activation
Immunology: Abbas Chapter 11 - Immunologic Tolerance
Immunology: Abbas Chapter 13 - Effector Mechanisms of Cell-Mediated Immunity
Cytokines and Their Receptors
Anticytokine Treatments for Asthma and Rhinitis
Immunology Jeopardy
Principles of Flow Cytometry
The Conferences On-Line Allergy (COLA) is a collaborative venture between the Children's Mercy Hospitals & Clinics section of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology and the American College of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology (ACAAI).
Questions and Answers
Abbas MCQ from FIT Corner by ACAAI, 2004.
The questions are posted in a reverse chronological order and you have to scroll to the bottom of the web page in order to see the first chapter.
Image source: Nutrophil, Wikipedia, GNU Free Documentation License.
Published: 02/01/2009
Updated: 03/04/2009
Free Lectures and Podcasts in Allergy and Immunology
 Author: V. Dimov, M.D., Allergist/Immunologist and Assistant Professor at University of Chicago
Author: V. Dimov, M.D., Allergist/Immunologist and Assistant Professor at University of ChicagoReviewer: S. Randhawa, M.D., Allergist/Immunologist and Assistant Professor at LSU (Shreveport) Department of Allergy and Immunology
Conferences On-Line Allergy (COLA)
Conferences On-Line Allergy (COLA) consists of the bi-weekly presentations at the Children's Mercy Hospitals & Clinics Section of Allergy, Asthma & Immunology. The lectures are very comprehensive and cover most of the spectrum of allergy and immunology. The project could be the video analog of the textbook Middleton's Allergy: Principles and Practice one day.
It is a good idea to download all video files (if allowed by the copyright holder) since many of the webmasters remove them after a certain period of the time. The download cane be done manually or throughiTunes by choosing the "Get all" option from the podcast menu.
Conferences On-Line Allergy (COLA) - free video lectures on allergy and immunology topics by ACAAI, YouTube channel
Allergy and Immunology Lectures at the University of South Florida
USF (University of South Florida, USA) Allergy & Immunology Lecture Series. The 55-minute lectures are recorded in wma format and are best viewed by using Windows Media Player software.
Conferences On-Line Allergy (COLA) - free video lectures on allergy and immunology topics by ACAAI, YouTube channel
Allergy and Immunology Lectures at the University of South Florida
USF (University of South Florida, USA) Allergy & Immunology Lecture Series. The 55-minute lectures are recorded in wma format and are best viewed by using Windows Media Player software.
Podcasts by Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology (JACI)
JACI Podcasts highlight recent publications in selected areas, and feature discussions with the authors, editors and other experts: http://www.jacionline.org/content/podcast
WAO Podcasts
Conversations with allergy experts are available as free MP3 files by the World Allergy Organization (WAO). You can subscribe to the RSS feed here: http://www.worldallergy.org/conversations/conversations.xml
The World Allergy Organization (WAO) Journal has a podcast section: Chief Editor Interviews.
Conversations with allergy experts are available as free MP3 files by the World Allergy Organization (WAO). You can subscribe to the RSS feed here: http://www.worldallergy.org/conversations/conversations.xml
ACAAI Conferences
- ACAAI Podcast and Vodcast Library is limited in scope but covers the latest advances in clinical allergy and immunology.
Immunology
The best resource seems to be the immunology course of the University of South Carolina. The lectures can be watched online or downloaded to aniPod/iPhone. Currently, there are 2 courses available -- from the year 2007 and 2008:
- Immunology 2007
- Immunology 2008
Archive of the Immunology Courses from University of South Carolina
Video Lectures in Immunology, LearnersTV.com
Immunology, University of Cambridge
Immunology I & II, MIT OpenCourseWare
Immunology: Lecture Series, Howard Hughes Medical Institute
Asthma
Allergic Rhinitis & Asthma. David Lang, MD. Drexel University College of Medicine Grand Rounds, 2003.
Severe Asthma: Clinical and Pathophysiologic Factors. Sally Wenzel, M.D. Drexel University College of Medicine Grand Rounds, 1999.
Asthma. Podcasts by the supplier of continuing medical education activities PeerView Press.
Allergic Rhinitis
Allergic Rhinitis. Podcasts by the supplier of continuing medical education activities PeerView Press.
Related Resources
Webinar Archives of World Allergy Organization (WAO)
Podcasts in Allergy and Immunology. Allergy Notes, 01/2008.
Immunology Resources: Audio and Video Lectures, PowerPoint Presentations, Q&A
Fellows-in-Training: Review Corner Archive, 2002-2008 by ACAAI
Published: 01/31/2008
Updated: 09/19/2011
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)